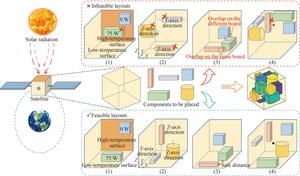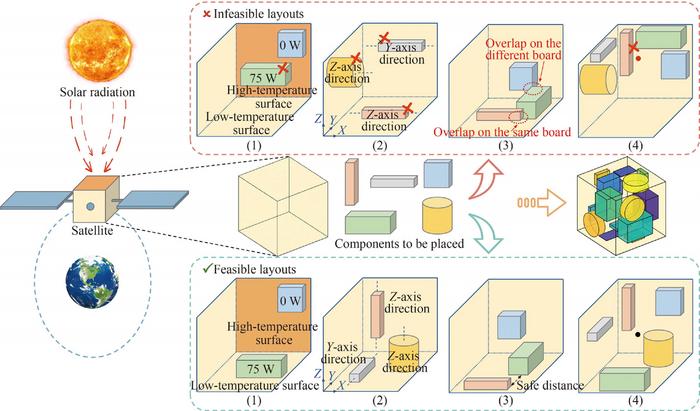
Picture:
The aim of the 3D scalo problem is to assign optimal fastening surfaces to the specified components and to position them in the best areas, while the requirements for (1) performance of the heat discharge, (2) Restriction of the special component position, (3) Component 3D Geome restriction and (4) Static restriction.
View more
Credit: Chinese Journal of Aeronautics
In satellite system design, optimizing the component layout is crucial for improving satellite performance. Recently, a research team led by Professor Wen Yao from the Defense Innovation Institute of the Chinese Academy for Military Science has made new progress in the field of 3D satellite components -layout optimization. This innovative approach can quickly offer engineers with high -quality layout candidates for components and to improve promise, efficiency and effectiveness of space.
Research, Published in the Chinese Journal of Aeronauticsintroduces a new satellite-triminal component allocation and layout optimization problem (3D scalo) from the practical technical requirements that takes the performance of the heat department as objective and the component 3D geome restrictions, the restrictions on the system stability and the restrictions of the special components for the components.
“The conventional optimization of the satellite layout has been strongly based on manual methods that are not only time -consuming, but also prevents us from completely exploring the potential of the design space,” said Yufeng Xia, the first author of the paper. “With increasingly complex and diverse satellite missions, the development has become an urgent challenge.”
The 3D scalo problem is a challenging bilevel-combinatorial optimization task, which includes the optimization of discreet component assignment variables in the outer layer and the variables of the position of continuous components in the inner layer, with both influence on each other. In order to tackle this problem, the research team proposed a MIP model (mixed integer programming). It transformed the original problem of bilevel optimization into one-stage single-stage, whereby the optimization of the discrete component assignment and the continuous detailed position optimization were modeled into comprehensive formulation, which generates the layout design in a single run and complex iterations of the complex nested optimization were avoided.
In order to tackle the challenge of modeling geometric 3D relationships within the MIP framework, the researchers proposed a linearized 3D phi function method that explicitly and effectively processes overlapping and safety restrictions between the cuboid components. On this basis, the Finite Rightsk Method (FRM) was further proposed to remedy the geometric 3D restrictions between complex components and to expand the applicability of the method.
The research team checked the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed model using two numerical examples and a real engineering case. The results showed that the method could find optimal solutions in a reasonable time frame. In a technical case with 27 components in 5 modules, the model found the optimal solution in 193.5 seconds and completely demonstrated its applicability in complex technical applications.
The research team states that from the perspectives of problem modeling, analysis and optimization algorithms to provide more efficient solutions, continue to research incoming research on the 3D scalo problem and thus drive the intelligent design of space vehicles.
Other participants are Xianqi Chen and Weiien Zhou from the Defense Innovation Institute of the Chinese Academy for Military Science in Beijing, China; Zhijia Liu from DFH Satellite Co., Ltd. in Beijing, China; and Zhongneng Zhang from College of Aerospace Science and Engineering at the National University of Defense Technology in Changsha, China.
Original source
Yufeng Xia, Xianqi Chen, Zhijia Liu, Weiien Zhou, Wen Yao, Zhongneng Zhang. Mixed full number programming model for the three-dimensional satellite component assignment and layout optimization problem[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics2025, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2025.103415
Around Chinese Journal of Aeronautics
Chinese Journal of Aeronautics (CJA) is an open access, by experts examined international journal, which covers all aspects of aerospace engineering that was published by Elsevier every month. The journal reports on the scientific and technological achievements and borders in aviation technology and in astronaut technology, both in theory and in practice. Cja is indexed in sci (if = 5.3, top 4/52, Q1), egg, iaa, aj, csa, scopus.
magazine
Chinese Journal of Aeronautics
Article title
Mixed full number programming model for the three-dimensional satellite component assignment and layout optimization problem
Article publication date
22-jan-2025
Liability exclusion: Aaas and Eurekalert! are not responsible for the accuracy of news publications published in Eurekalert! through contributions from institutions or the use of information about the Eurekalert system.